System Design for Everyone: A Primer On Sharding (Ft. MongoDB)
If a database had more databases.
Target: Pre-senior engineer
📚 tldr;
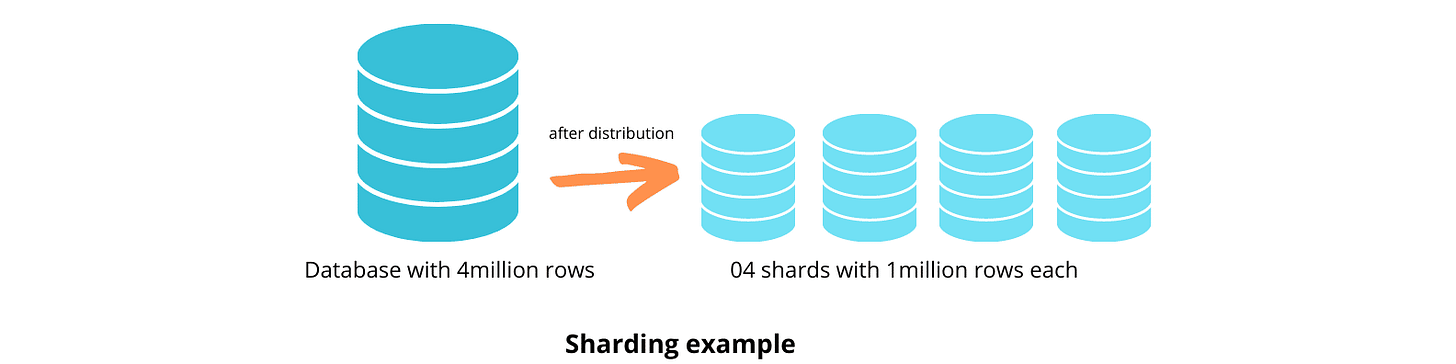
Sharding just means spliting up a database into smaller databases. You only have to do this if you can’t put everything on one database server.
🙏 Please explain “Sharding“
Sharding is a fancy word. What it actually is isn’t fancy.
Sharding
Break down a single dataset across multiple databases.
Example
Instead of putting 10,000,000 users in one database, you can break that down to 5,000,000 million users across two databases.
Yes, this is a form of horizontal scaling.
💬 When Would I Even Use This?
If your database has a ton of data and has too many requests, here are your options:
Vertical Scaling - Just make the database stronger by adding more RAM, CPU, Disk.
Except this costs $$$ to implement.Horizontal Scaling - Just add more machines to share the dataset and the work load.
Except this gets complicated to implement.
So if you’re working on HUGE applications, knowing how to shard the database can keep you up and running.
📖 Ok, Teach me How to Shard
Distribute the Data
If sharding means breaking up a dataset, then we need to talk about how we would do that.
🏹 Ranged Based Sharding
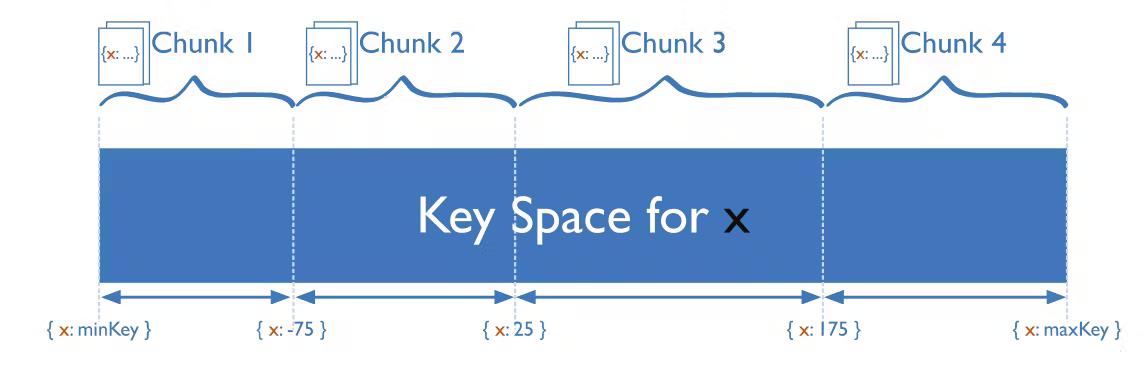
Define how many shards you have and give each a range. If a database record (like a user id) is in that range, send it to that shard.
Shard A: User IDs [0, 20]
Shard B: User IDs [21, 40]
Shard C: User IDs [41, 50]
You can see how the key space is broken down into 4 chunks (shards) above. If a data record is in one of those ranges, it’ll be sent to that shard.
🚨 Watch Out: Make sure the ranges you’re using is equally distributed. Otherwise everything will end up on one shard and slow down performance.
🥔 Hashed Based Sharding
Just use the database record mod number of shards (% total shards)
Shard to Send To = some ID % total shards
It’s almost like range-based sharding except it makes it easier to distribute everything evenly.
🚨 Watch Out: If a record is huge and needs to be split, it can end up on a different shard. Finding that other shard can be difficult.
The other problem is that if the total number of shards needs to be added or removed, then you’ll have to rebalance all your database records.
That’s going to cause a system outage and that’s not a fun time.
🌎 Geography Based Sharding
Keep reading with a 7-day free trial
Subscribe to Byte-Sized Design to keep reading this post and get 7 days of free access to the full post archives.